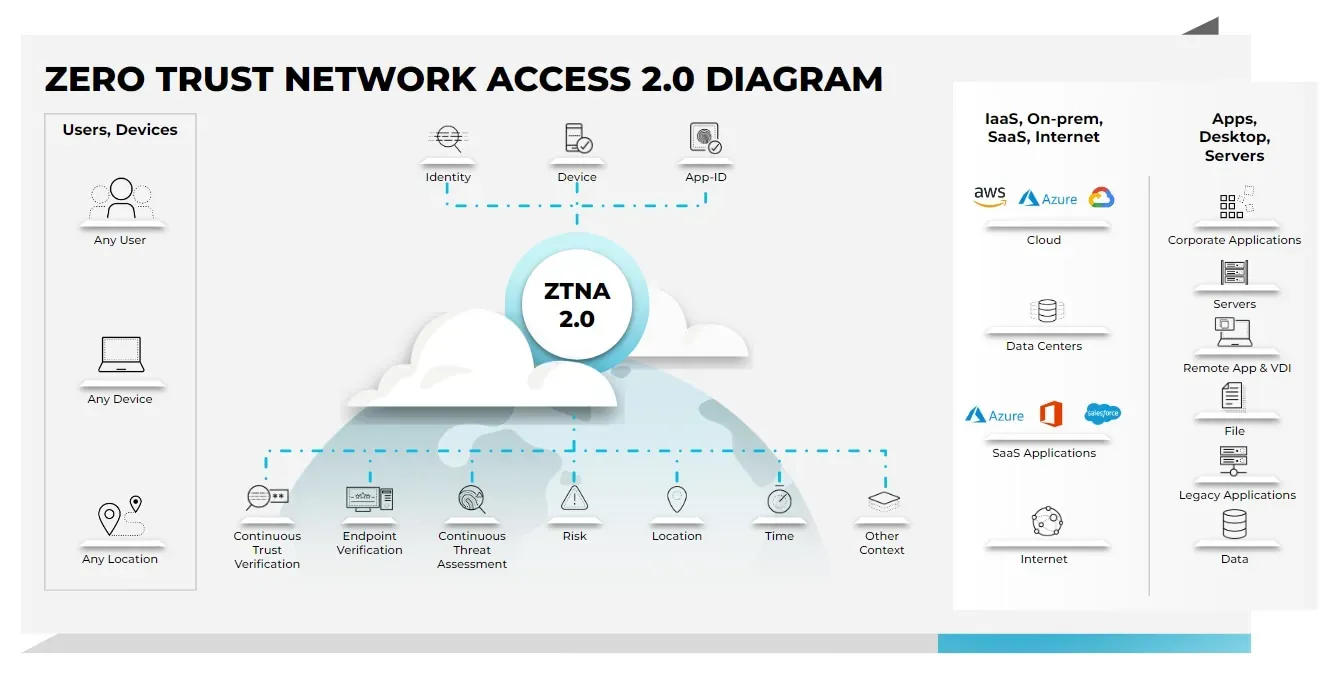
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is rapidly becoming a fundamental strategy for organizations looking to enhance their cybersecurity posture in today’s digital landscape. As cyber threats continue to evolve and expand, traditional security measures are proving insufficient, necessitating a shift towards more dynamic approaches. ZTNA redefines how access to network resources is managed, fundamentally operating on the principle that no user or device should be trusted by default, regardless of their location. This rigorous verification process not only strengthens network security but also aligns with broader trends in digital transformation and remote work. By adopting Zero Trust Network Access, businesses can implement effective cybersecurity strategies that align with network security best practices, ensuring sensitive information remains protected against unauthorized access.
The concept of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), often referred to as zero trust architecture or zero trust security, represents a revolutionary shift in how organizations secure their networks. In an era where digital transformation is reshaping business operations, the traditional perimeter-based security models are increasingly inadequate. Instead, zero trust frameworks advocate for a comprehensive verification process for every access request, whether it originates from within the organization’s physical boundaries or from remote locations. By implementing principles such as continuous authentication and least privilege access, companies can significantly bolster their defenses against cyber threats. This proactive approach not only enhances overall security but also supports the implementation of network security best practices, ensuring that organizations can navigate the complexities of modern cybersecurity challenges.
Understanding Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a revolutionary approach to cybersecurity that moves away from traditional perimeter defenses. In today’s landscape, where remote work is increasingly prevalent, ZTNA provides a framework that ensures every access request is treated as potentially risky, regardless of its origin. This model is built on the principle of ‘never trust, always verify,’ which means that every user and device must be authenticated and continuously validated before being granted access to sensitive data. This approach significantly enhances an organization’s security posture by minimizing the chances of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Moreover, the implementation of ZTNA aligns with modern cybersecurity strategies that prioritize data protection over network boundaries. By leveraging technologies such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), identity verification, and real-time monitoring, organizations can create a more secure environment. The focus on continuous verification enables businesses to adapt to the evolving threat landscape while ensuring that user experience is not adversely affected. ZTNA represents a critical shift in how companies think about network security, emphasizing the importance of protecting data above all else.
Key Principles of ZTNA Implementation
The successful implementation of Zero Trust Network Access hinges on several core principles that organizations must embrace. Continuous verification is paramount; every access attempt is rigorously assessed to ensure that only authorized users and devices gain entry to sensitive systems. This approach counters the vulnerabilities associated with traditional security models, which often assume that once inside the network, a user is trustworthy. By consistently validating access requests, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches stemming from compromised credentials.
Another fundamental principle of ZTNA is the concept of least privilege access. This means that users are granted the minimum level of access necessary to perform their job functions. By limiting access rights, organizations can decrease the attack surface and protect critical assets. Micro-segmentation is also an important strategy within ZTNA, as it involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, which helps contain potential breaches and prevents lateral movement by attackers. Together, these principles form a robust framework that enhances overall network security.
ZTNA versus Traditional Security Models
When comparing Zero Trust Network Access to traditional security models, the differences are striking. Traditional models often rely on a strong perimeter defense, assuming that users inside the network can be trusted. This assumption is increasingly outdated in light of sophisticated cyber threats. ZTNA, on the other hand, operates on the premise that every access request, whether internal or external, is suspect. This shift in mindset ensures that organizations remain vigilant against both external attacks and insider threats.
Furthermore, ZTNA aligns seamlessly with the needs of organizations that are heavily reliant on cloud services. As more businesses move to remote work and cloud-based solutions, the traditional perimeter becomes less relevant. ZTNA offers a flexible and adaptive security model that is inherently designed to protect sensitive data in a cloud-first world. By implementing ZTNA, organizations can ensure that their security strategies are proactive and capable of mitigating risks associated with the evolving digital landscape.
Implementing ZTNA: Strategic Steps
Implementing Zero Trust Network Access requires careful planning and execution. The first step is to evaluate the current infrastructure to identify vulnerabilities and existing access controls. This thorough assessment lays the groundwork for a successful ZTNA adoption, ensuring that organizations understand their security landscape before making changes. Identifying critical assets is also essential; organizations must pinpoint which data and applications require the highest level of protection to prioritize their ZTNA efforts effectively.
Choosing the appropriate ZTNA solutions is another crucial step. With a plethora of options available, organizations need to select tools that align with their specific security needs and institutional objectives. For organizations heavily utilizing cloud services, opting for cloud-native ZTNA solutions can enhance security and efficiency. Finally, seamless integration of ZTNA solutions into existing workflows and ongoing monitoring of the system’s performance are vital for maintaining security effectiveness and adapting to new threats.
Enhancing User Experience with ZTNA
A common concern regarding the adoption of Zero Trust Network Access is its potential impact on user experience. With stringent verification processes, users may fear that their ability to access resources will be hindered. However, when ZTNA tools are thoughtfully designed and integrated, they can actually improve the user experience. Modern ZTNA solutions utilize advanced algorithms to analyze user behavior patterns, allowing for a more streamlined authentication process that reduces unnecessary friction for end-users.
By balancing rigorous security measures with user convenience, organizations can create a seamless experience without compromising on safety. For instance, adaptive authentication methods can minimize the frequency of authentication prompts while still ensuring that access remains secure. This thoughtful approach to ZTNA implementation not only protects sensitive data but also fosters a more positive experience for employees, ultimately enhancing productivity and satisfaction.
The Future of Zero Trust Network Access
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the future of Zero Trust Network Access looks promising. The rise of remote work and digital transformation has increased the importance of robust cybersecurity measures, making ZTNA a foundational strategy for organizations looking to safeguard their assets. By adopting ZTNA principles, companies can establish a security framework that is adaptable to changing conditions and threats, ensuring they remain resilient in the face of evolving cyber challenges.
Looking ahead, organizations will likely see an increasing emphasis on integrating ZTNA with other cybersecurity strategies, such as endpoint security and threat intelligence. This holistic approach will enable businesses to create a comprehensive security posture that not only protects against unauthorized access but also proactively addresses potential vulnerabilities. By investing in ZTNA and continuously refining their security practices, organizations can better prepare for the future of cybersecurity and maintain a competitive edge in an interconnected world.
Micro-Segmentation in ZTNA
Micro-segmentation is a crucial component of Zero Trust Network Access that plays a significant role in enhancing network security. By dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, organizations can limit the lateral movement of attackers within their systems. This strategy confines breaches to a single segment, making it easier to contain and mitigate potential threats. Micro-segmentation allows for tailored security policies to be applied to each segment, ensuring that sensitive data is protected according to its specific risk profile.
Additionally, implementing micro-segmentation can help organizations comply with regulatory requirements by providing a more granular level of control over data access. This approach not only strengthens overall security but also aids in maintaining audit trails and monitoring user activity within each segment. As part of a broader Zero Trust strategy, micro-segmentation enhances an organization’s ability to respond to emerging threats while ensuring that critical assets remain secure.
Cybersecurity Strategies in the Era of ZTNA
In the era of Zero Trust Network Access, organizations must adapt their cybersecurity strategies to align with the principles of continuous verification and least privilege access. Traditional approaches that rely heavily on perimeter security are becoming ineffective against sophisticated cyber threats. To remain resilient, organizations should incorporate ZTNA into their overall security framework, emphasizing the importance of validating every access request, regardless of the user’s location or device.
Moreover, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity strategies by integrating ZTNA with advanced threat detection technologies and incident response plans. By combining these elements, businesses can create a proactive security posture that not only defends against external threats but also minimizes the risk of insider attacks. As the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, embracing ZTNA will be essential for organizations seeking to protect their critical assets and maintain a strong security stance.
Best Practices for Zero Trust Implementation
To successfully implement Zero Trust Network Access, organizations should adhere to best practices that ensure a smooth transition from traditional security models. First and foremost, it is essential to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the existing security infrastructure. By identifying vulnerabilities and understanding current access controls, organizations can create a tailored ZTNA strategy that aligns with their unique needs and objectives. This foundational step sets the stage for effective implementation.
Another key best practice involves continuous monitoring and adaptation of security policies. As new threats emerge and organizational needs change, it is vital to reassess access controls and adjust permissions accordingly. Regularly updating security protocols and employing automated tools for monitoring can help organizations stay ahead of potential risks. By consistently refining their ZTNA implementation, organizations can strengthen their overall security posture and effectively safeguard sensitive data.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and how does it enhance cybersecurity?
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a security framework that requires strict verification for every access request, regardless of the user’s location. Unlike traditional security models that trust users once they are inside the network perimeter, ZTNA’s ‘never trust, always verify’ approach enhances cybersecurity by continuously authenticating users and devices, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information.
How can organizations implement ZTNA effectively?
To implement Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) effectively, organizations should start by evaluating their current infrastructure, identifying critical assets that require protection, and selecting appropriate ZTNA solutions that align with their security needs. Integration of these solutions should be seamless, and ongoing monitoring is essential to adapt to evolving threats and organizational changes.
What are the core principles of ZTNA that organizations should follow?
The core principles of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) include ‘never trust, always verify’ which ensures continuous authentication, ‘least privilege access’ that limits user permissions to only what is necessary, and ‘micro-segmentation’ which divides the network into smaller zones to contain potential breaches. These principles work together to enhance overall network security.
How does ZTNA compare to traditional security measures?
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) contrasts sharply with traditional security measures that often rely on a perimeter-based approach. While conventional systems grant broad access once inside the network, ZTNA treats every access request as potentially risky, requiring rigorous verification to ensure that only authenticated users and devices can access sensitive resources.
Does implementing ZTNA impact user experience negatively?
While there are concerns that Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) may hinder user experience due to stringent verification processes, well-designed ZTNA solutions can actually enhance it. Advanced algorithms can analyze user behavior to reduce unnecessary authentication steps, allowing for smoother transitions while maintaining high security standards.
What role does ZTNA play in digital transformation for organizations?
In the context of digital transformation, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) plays a crucial role by providing a robust security framework that protects sensitive data while enabling flexible access for remote employees. This adaptability is vital as organizations navigate complex digital environments and strive to maintain strong cybersecurity practices amidst evolving threats.
What are some network security best practices when implementing ZTNA?
When implementing Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), best practices include conducting thorough infrastructure assessments, prioritizing the protection of critical assets, selecting the right ZTNA solutions that fit organizational needs, ensuring seamless integration, and maintaining ongoing monitoring to respond quickly to emerging security challenges.
How does micro-segmentation work within a ZTNA framework?
Micro-segmentation within a Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) framework involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments. This limits lateral movement within the network for potential intruders, effectively containing breaches and enhancing the overall security posture by ensuring that access to sensitive information is tightly controlled and monitored.
| Key Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Never Trust, Always Verify | No entity is inherently trusted; continuous authentication is required for all access requests. |
| Least Privilege Access | Users are granted only the permissions necessary for their roles, minimizing potential damage from compromised accounts. |
| Micro-Segmentation | Network is divided into isolated zones to limit lateral movement of intruders during a breach. |
| ZTNA vs Traditional Security | ZTNA treats all access attempts as suspicious, requiring verification, unlike traditional models that trust internal users by default. |
| Implementing ZTNA | Requires assessing current infrastructure, identifying critical assets, choosing appropriate solutions, and ongoing monitoring. |
| User Experience with ZTNA | Well-designed ZTNA solutions can enhance user experience by minimizing unnecessary authentication steps through behavior analysis. |
Summary
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is pivotal in ensuring cybersecurity in the modern digital age, especially as cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated. By implementing ZTNA principles, organizations can create a robust security framework that continuously verifies access requests, minimizes trust assumptions, and enforces strict access controls. This proactive approach not only protects sensitive data but also aligns security measures with the evolving landscape of remote work and cloud computing. As businesses continue to adapt to these changes, adopting ZTNA will be essential for safeguarding digital assets and maintaining compliance with regulatory standards.