Apple iCloud data encryption has become a hot topic in the wake of the UK government’s demands for access to customer information. In an effort to comply with these demands, Apple has decided to disable its Advanced Data Protection (ADP) end-to-end encryption for users in the UK, raising significant concerns regarding data privacy. This controversial move highlights the ongoing struggle between government oversight and individual privacy rights, especially as data breaches continue to rise. Apple maintains its commitment to safeguarding user information, emphasizing that some data like health records and messages will still enjoy encryption protection. However, this decision affects numerous iCloud services, prompting users to question the effectiveness of Apple privacy features in the current security landscape.
The encryption of data stored in Apple’s iCloud has gained attention due to recent governmental pressures for data access. This situation has led to the suspension of Apple’s Advanced Data Protection features for users in the UK, igniting debates about privacy and security. As similar scenarios unfold globally, understanding the implications of such decisions is crucial for users concerned about their digital safety. While some aspects of iCloud still benefit from encryption, the new limitations raise alarms about data breach prevention and the potential risks users face. The ongoing evolution of iCloud security updates is essential to maintaining user trust amid these challenges.
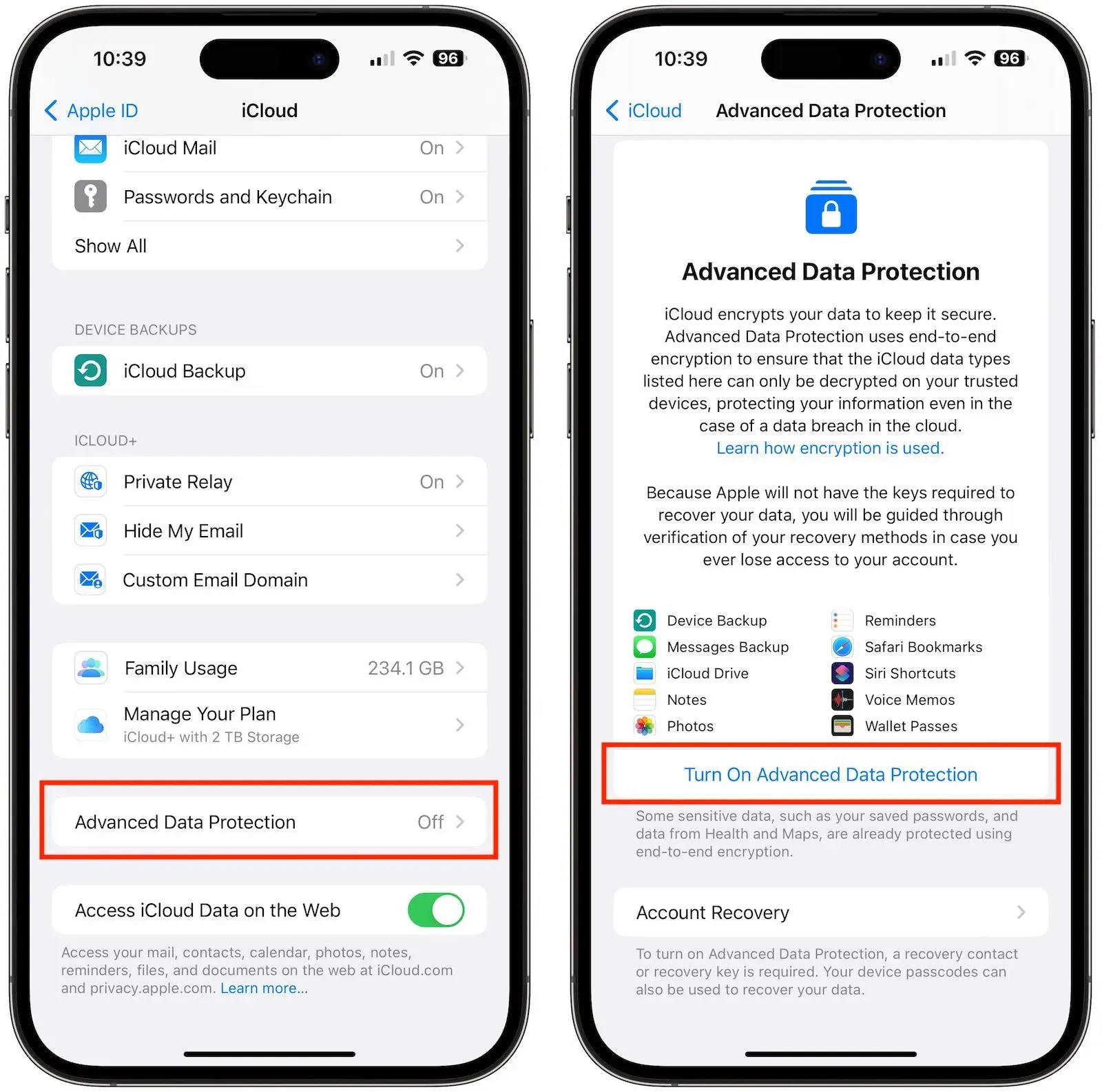
Apple’s Decision on Advanced Data Protection for UK Users
Apple’s recent decision to turn off its Advanced Data Protection (ADP) end-to-end encryption for UK users has raised alarms regarding data security. The UK government’s demands for backdoor access to customer data have forced Apple to compromise on its privacy features, which are designed to protect user information from unauthorized access. This move not only affects the strong encryption that ADP provides but also sets a concerning precedent for how corporations might respond to governmental pressures surrounding data access.
Despite the loss of ADP protection, Apple reassured its users that certain types of data, like health information and iMessages, remain encrypted. However, a significant portion of user data stored in iCloud, such as backups and notes, is now vulnerable. This situation highlights the ongoing conflict between user privacy rights and government surveillance, raising questions about the adequacy of current data protection laws in the UK context.
Implications of UK Government Data Access Requests
The UK government’s push for access to personal data stored by tech companies under the Investigatory Powers Bill has sparked significant debate over privacy rights versus national security. Proponents argue that such access is necessary for law enforcement to combat crime and terrorism effectively. However, this has raised concerns about potential abuse of power and the erosion of civil liberties. The challenge lies in finding a balance that allows for effective law enforcement while safeguarding individual privacy.
As Apple turns off its ADP feature, users in the UK are left with diminished security and less control over their personal information. This situation could serve as a wake-up call for consumers to demand stronger privacy protections from their service providers. In light of these developments, it is critical for both consumers and advocacy groups to remain vigilant and engaged in discussions about data protection and privacy legislation.
The Role of Apple Privacy Features in Data Security
Apple’s privacy features have always been at the forefront of its brand identity, designed to give users control over their data and enhance security. Features like Face ID, two-factor authentication, and end-to-end encryption have made iCloud and other Apple services secure. However, the recent decision to disable Advanced Data Protection for UK users raises critical questions about the effectiveness of these privacy features when faced with governmental demands. As Apple navigates these challenges, the effectiveness and integrity of its privacy features may come under scrutiny.
The ongoing developments also underscore the importance of encryption in protecting user data from breaches and unauthorized access. With the rise of data breaches across various sectors, users increasingly rely on robust privacy features to safeguard their information. Apple’s commitment to not creating backdoors in its products is commendable, yet the inability to offer full encryption in certain regions poses a significant risk to customer privacy and trust in the brand.
iCloud Security Updates: What Users Need to Know
In light of Apple’s recent changes to iCloud security protocols, users should be aware of the implications for their data protection. While some aspects of data stored in iCloud will still benefit from end-to-end encryption, many important features will not. This change means that sensitive information, such as backups and notes, is now more vulnerable to unauthorized access, particularly in light of increasing data breaches across various platforms. Users must take proactive steps to ensure their data remains secure.
Apple’s decision to disable ADP for UK users highlights the need for ongoing vigilance in data security practices. Users should regularly review their iCloud settings, utilize strong passwords, and enable two-factor authentication to enhance their security. Additionally, keeping abreast of updates from Apple regarding iCloud security will help users make informed decisions about their data protection strategies.
Data Breach Prevention: Lessons from Apple’s Situation
The situation faced by Apple in the UK serves as a crucial lesson in data breach prevention and the importance of robust security measures. As governments worldwide continue to push for data access for security purposes, companies must evaluate their data protection strategies to mitigate risks. Apple’s strong stance against backdoor access is commendable, but the compromise of its Advanced Data Protection feature shows that even the most secure systems are vulnerable to external pressures.
Organizations should take this incident as an opportunity to reassess their own data security policies. Implementing multi-layered security measures, conducting regular audits, and fostering a culture of security awareness among employees can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches. Additionally, companies must advocate for stronger privacy regulations that protect user data from unnecessary governmental intrusion.
UK Data Privacy Regulations: An Overview
The UK has been navigating complex data privacy regulations, particularly following the implementation of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). These regulations are designed to protect individuals’ personal data and impose strict penalties for breaches. However, the recent demands from the UK government for access to customer data highlight a tension between regulatory compliance and individual privacy rights. Understanding these regulations is crucial for both consumers and businesses to navigate the evolving landscape of data protection.
In the wake of Apple’s decision to disable its Advanced Data Protection feature, it is essential for users to remain informed about their rights under UK data privacy laws. This includes the right to access personal data, the right to erasure, and the right to data portability. Consumers should be empowered to demand transparency from companies about how their data is used and protected, fostering a more secure digital environment.
The Future of Encryption in the UK
The recent developments surrounding Apple’s encryption policies in the UK raise important questions about the future of encryption technology in the country. As privacy advocates express concern over government access to personal data, the need for robust encryption solutions becomes even more critical. The ability to protect user data through advanced encryption techniques is paramount to ensuring that individuals can maintain their privacy in an increasingly surveilled world.
Moving forward, it is likely that the debate over encryption will intensify, with calls for stronger protections against government overreach. As technology continues to evolve, so too should the measures put in place to safeguard user data. Companies like Apple must lead the charge in advocating for user privacy while finding ways to comply with regulations that do not compromise the integrity of their security systems.
Consumer Awareness in Data Security
In an era where data breaches are becoming increasingly common, consumer awareness regarding data security is more important than ever. Understanding how personal data is collected, stored, and used is essential for making informed decisions about digital services. As seen in Apple’s recent changes to iCloud security, consumers must be proactive in protecting their information and aware of the implications of using services that may not prioritize their privacy.
Educating oneself about the privacy features offered by different service providers is a critical step for consumers. Evaluating the security measures in place, such as encryption protocols and data access policies, can help individuals choose services that align with their privacy values. As consumers become more informed, they can advocate for better data protection practices and push for regulations that prioritize user privacy.
Government Surveillance vs. User Privacy: A Delicate Balance
The ongoing debate between government surveillance and user privacy is a complex issue that continues to evolve. The demand for backdoor access to user data by the UK government poses a significant challenge to privacy advocates, who argue that such measures compromise individual freedoms. The balance between ensuring national security and protecting citizens’ rights is a delicate one, requiring careful consideration and dialogue among stakeholders.
As companies like Apple navigate these challenges, it is vital for policymakers to engage in thoughtful discussions about the implications of surveillance on privacy rights. Finding a balance that protects citizens while allowing law enforcement to perform their duties is crucial for maintaining public trust in both technology and government. Continued advocacy for strong privacy protections is essential to ensure that user rights are upheld in the face of increasing surveillance demands.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Apple iCloud data encryption and how does it protect my data?
Apple iCloud data encryption refers to the security measures employed by Apple to safeguard user data stored in iCloud. With features like Advanced Data Protection (ADP), Apple offers end-to-end encryption (E2EE) for certain types of data, ensuring that only the user has access to their information. This means that even Apple cannot access the data, which enhances privacy and security.
How does the UK government’s data access demand affect Apple iCloud data encryption?
The UK government’s demand for access to customer data has led Apple to disable Advanced Data Protection (ADP) for UK users. Consequently, users in the UK will no longer benefit from the enhanced security of end-to-end encryption, allowing both Apple and law enforcement to access certain data without a backdoor.
What data is still protected by Apple iCloud’s encryption features?
Despite the recent changes due to UK regulations, some data in iCloud remains protected by Apple’s encryption. This includes health information, iMessages, and FaceTime calls. However, iCloud backups, photos, and other data types are no longer protected by Advanced Data Protection in the UK.
What are the implications of disabling Advanced Data Protection for UK iCloud users?
Disabling Advanced Data Protection for UK users means reduced security for their iCloud data. Users will have less protection against potential data breaches, as many types of data will no longer be secured by end-to-end encryption, making it accessible to Apple and law enforcement with proper legal requests.
What are the latest iCloud security updates from Apple regarding data encryption?
Apple’s latest iCloud security updates indicate that Advanced Data Protection has been turned off for users in the UK due to government pressures. This change affects how data is encrypted and accessed, significantly lowering the level of security previously available to these users.
How does Apple prioritize data breach prevention with iCloud data encryption?
Apple emphasizes data breach prevention through its robust encryption protocols, particularly with Advanced Data Protection. By ensuring that sensitive data is encrypted end-to-end, Apple aims to protect users from unauthorized access and potential breaches, although recent changes in the UK have altered this landscape.
What privacy features does Apple offer in relation to iCloud data encryption?
Apple offers several privacy features related to iCloud data encryption, including Advanced Data Protection for end-to-end encryption of specific data types, and strong security measures like two-factor authentication. These features aim to provide users with greater control over their personal data and enhance their overall privacy.
Can iCloud data be accessed without a backdoor, and how does this relate to encryption?
Apple has stated that it has never built a backdoor to access iCloud data and will not do so. This commitment to privacy means that, under normal circumstances, iCloud data is only accessible by the user through encryption. However, changes in the UK now allow law enforcement to access data with legal requests.
Is there any way for UK users to enhance their iCloud data encryption security?
While UK users can no longer utilize Advanced Data Protection for their iCloud data, they can enhance their security by using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and being cautious about the types of data they store in iCloud. Regularly reviewing security settings can also help ensure better protection.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Apple iCloud Data Encryption Policy Change | Apple turned off Advanced Data Protection (ADP) for UK users due to government demands. |
| Reason for Change | UK Home Office requested a backdoor for data access under Investigatory Powers Bill. |
| Impact of the Decision | ADP end-to-end encryption (E2EE) is no longer available for UK residents, affecting data security. |
| Data Still Protected | Some data like health information, iMessages, and FaceTime calls remain protected by E2EE. |
| Affected Data Types | iCloud backups, photos, notes, and other data types will lose encryption protection. |
| User Experience | UK users trying to enable ADP will see error messages; existing users must disable it. |
| Apple’s Stance | Apple stated it has never built a backdoor and aims to maintain customer privacy. |
Summary
Apple iCloud data encryption has undergone significant changes as the company has suspended its Advanced Data Protection (ADP) end-to-end encryption service for UK users following government pressure. This decision has raised concerns regarding user privacy and data security, especially as many types of data will no longer be protected. Apple maintains that it does not support backdoors, emphasizing its commitment to user privacy. However, the implications of this decision could lead to increased vulnerabilities for UK customers, highlighting the ongoing tension between privacy rights and governmental oversight.