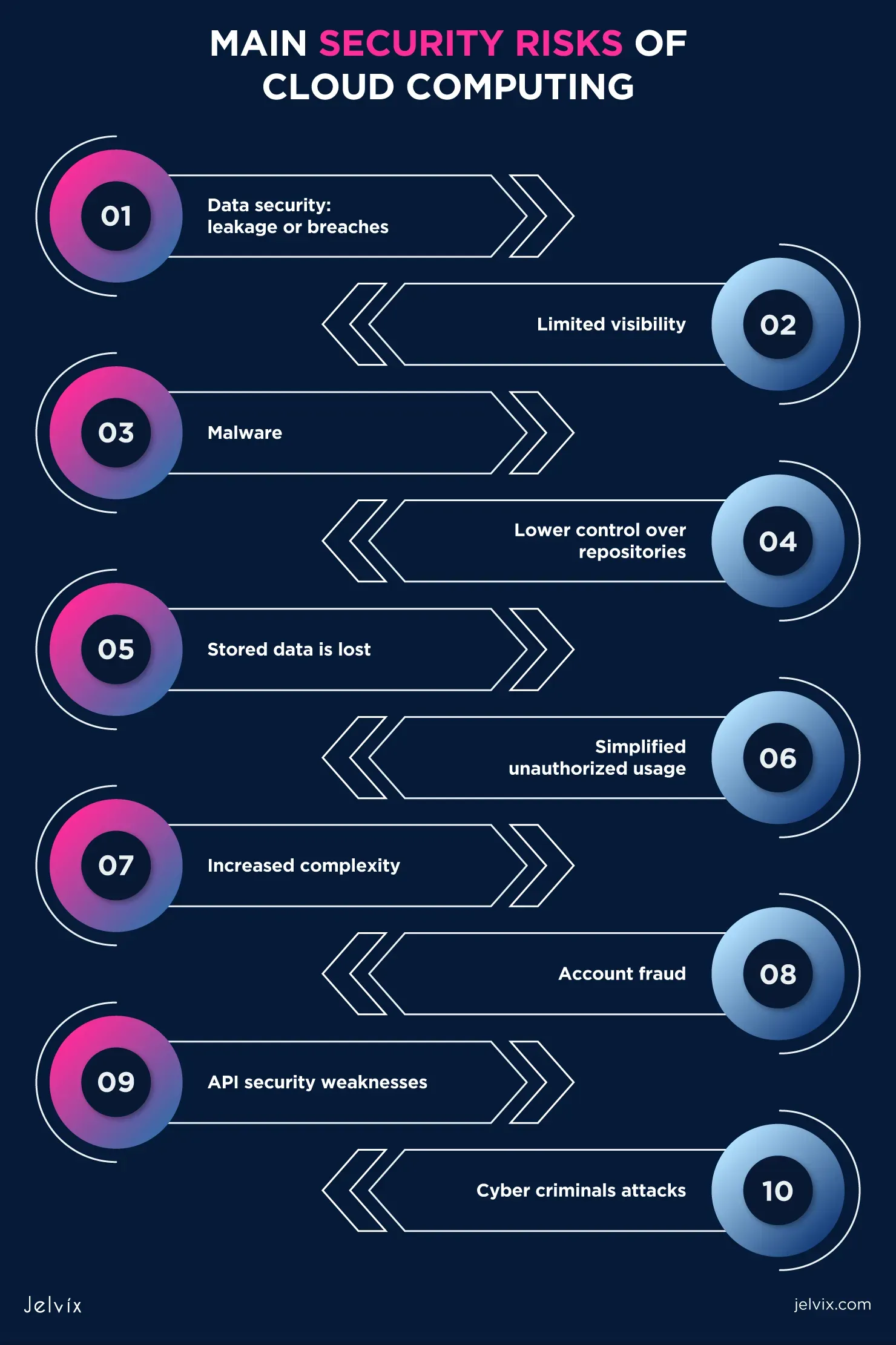
In today’s digital landscape, understanding the risks associated with cloud computing is essential for any organization looking to harness its power. As businesses increasingly migrate to the cloud, they must confront significant cloud computing risks that could jeopardize their data and operations. Issues such as cloud security vulnerabilities, cloud data breaches, and the challenges of cloud compliance can lead to dire consequences if not managed properly. Additionally, the complexities of identity access management and cloud vendor lock-in further complicate the security landscape. To navigate these risks effectively, organizations must adopt comprehensive strategies that prioritize robust security measures and compliance protocols.
The transition to digital solutions has ushered in a new era where reliance on remote servers and services, often referred to as cloud infrastructure, is at an all-time high. However, with this shift comes a set of challenges, including potential vulnerabilities in data protection, regulatory adherence, and the management of access controls. The risks associated with cloud technology can manifest as security breaches or compliance failures, placing sensitive information at risk. Moreover, organizations must be wary of the implications of dependency on specific cloud service providers, which can lead to restrictive vendor lock-in scenarios. Addressing these issues is crucial for businesses eager to leverage the benefits of cloud computing while safeguarding their assets.
Understanding Cloud Security Risks for 2025
As businesses increasingly migrate to cloud computing environments, understanding the landscape of cloud security risks is crucial. The rapid evolution of technology, coupled with the rising sophistication of cyber threats, means that organizations must be vigilant about securing their data. In 2025, some of the most pressing risks include data breaches, insufficient identity and access management, and compliance challenges. Organizations must prioritize these risks to safeguard sensitive data and maintain customer trust.
Cloud security is not just about protecting data; it encompasses a comprehensive strategy that includes implementing robust security measures, conducting regular audits, and staying informed about emerging threats. With cloud data breaches on the rise, companies must invest in advanced encryption methods, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring to mitigate these risks effectively. Failure to address these challenges can lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage.
The Impact of Data Breaches in Cloud Environments
Data breaches present one of the most significant risks associated with cloud computing. As organizations store sensitive information in the cloud, they become attractive targets for cybercriminals. Unauthorized access can result in the exposure of personal data, financial information, and trade secrets, leading to severe repercussions for both businesses and their clients. The consequences of a data breach extend beyond immediate financial losses; they can also lead to long-term damage to brand reputation and customer trust.
To combat the threat of data breaches, businesses must adopt a proactive approach to cloud security. Implementing strong encryption techniques, regular security audits, and employee training on cybersecurity best practices are essential steps in safeguarding data. Additionally, organizations should consider employing cloud access security brokers (CASBs) to monitor and enforce security policies across cloud services, thereby reducing the likelihood of data breaches and enhancing overall cloud security.
Navigating Compliance Challenges in Cloud Computing
Compliance with data protection regulations is a critical concern for organizations utilizing cloud services. With regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA imposing strict requirements on data handling and storage, failure to comply can result in hefty fines and sanctions. As more businesses transition to cloud environments, understanding and adhering to these regulations becomes increasingly complex. Organizations must stay updated on regulatory changes and implement necessary adjustments to their cloud security policies.
To effectively navigate compliance challenges, businesses should leverage compliance automation tools that continuously monitor adherence to regulations. Conducting regular compliance audits and risk assessments can help organizations identify potential gaps in their processes. Furthermore, employee training on regulatory requirements ensures that all staff members understand their roles in maintaining compliance in the cloud.
Mitigating the Risks of Insecure APIs
Insecure APIs represent a significant vector for cyberattacks in cloud computing environments. As organizations integrate third-party applications and services into their cloud infrastructure, the need for robust API security becomes paramount. Weak or misconfigured APIs can lead to unauthorized access and data leakage, posing serious risks to cloud security. Therefore, businesses must prioritize securing their APIs to prevent potential breaches.
To mitigate the risks associated with insecure APIs, organizations should implement strict authentication measures, such as token-based access controls. Regular security scans and vulnerability assessments are essential to identify and address potential weaknesses in API configurations. Additionally, adopting best practices for API development, such as input validation and error handling, can further enhance security and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Understanding Cloud Vendor Lock-In Risks
Cloud vendor lock-in occurs when organizations become overly dependent on a single cloud provider, creating challenges for data portability and flexibility. This situation can lead to increased operational risks, higher costs, and diminished control over cloud resources. As businesses scale and evolve, the inability to switch providers easily can hinder their growth and innovation. Understanding these risks is essential for organizations looking to optimize their cloud strategies.
To avoid the pitfalls of vendor lock-in, companies should consider adopting a multi-cloud strategy that allows them to distribute workloads across multiple cloud providers. This approach not only enhances resilience but also provides organizations with leverage when negotiating contracts. Regularly evaluating cloud performance and maintaining a flexible architecture can help businesses remain agile and responsive to changing market conditions.
The Threat of DDoS Attacks on Cloud Services
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks pose a significant threat to cloud services, potentially disrupting operations and damaging an organization’s reputation. As cybercriminals continue to develop more sophisticated attack methods, the risk of DDoS attacks on cloud infrastructure grows. These attacks can overwhelm cloud resources, rendering them unavailable to legitimate users and causing financial losses.
To protect against DDoS attacks, businesses should utilize mitigation tools provided by their cloud service providers. Implementing Web Application Firewalls (WAF) can help filter out malicious traffic and ensure that legitimate users can access cloud services. Additionally, organizations should develop and regularly test DDoS response plans to ensure they are prepared to respond quickly and effectively to any attacks.
The Risks of Insecure Third-Party Integrations
As businesses increasingly rely on third-party applications integrated into their cloud environments, the risk of cyberattacks grows. If these third-party providers lack robust security measures, they can expose organizations to significant vulnerabilities. Insecure third-party integrations can lead to data breaches, compliance issues, and operational disruptions, making it essential for businesses to manage their vendor relationships effectively.
To mitigate the risks associated with third-party integrations, organizations should conduct thorough security assessments of their vendors and establish a robust vendor risk management framework. Regularly reviewing the security controls of third-party applications and enforcing security requirements in contracts can help safeguard sensitive data. By prioritizing third-party security, businesses can reduce their attack surface and enhance overall cloud security.
Effective Strategies for Data Loss Prevention
Data loss remains a critical concern for organizations leveraging cloud services. Despite the redundancy often promised by cloud providers, accidental deletions, cyberattacks, and outages can lead to permanent data loss. Without proper backup and recovery strategies, businesses risk losing valuable information that can impact operations and customer trust.
To prevent data loss, organizations should implement comprehensive backup solutions, including version control and regular data snapshots. Developing and testing a disaster recovery plan ensures that businesses can quickly recover from data loss incidents. Additionally, investing in redundancy planning can help maintain data availability, providing peace of mind in the face of unexpected threats.
Emerging Threats from AI and Automation in Cloud Security
As artificial intelligence (AI) and automation become more integrated into cloud computing, new security threats are emerging. Cybercriminals are leveraging AI to develop advanced attack methods, including automated phishing campaigns and sophisticated malware. These AI-driven threats pose significant challenges for organizations, making it essential to adopt proactive security measures.
To combat emerging threats from AI, businesses should implement AI security frameworks that utilize machine learning to detect anomalies and potential breaches. Conducting thorough testing of AI models before deployment can help identify vulnerabilities. Moreover, continuous monitoring of automated processes is crucial to ensure that any unusual activities are quickly addressed, thereby safeguarding cloud environments from evolving threats.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Cloud Security in 2025
As we approach 2025, the landscape of cloud computing risks continues to evolve. Organizations must prioritize cloud security to mitigate threats to their data, systems, and overall reputation. By understanding the top cloud computing risks and implementing proactive measures, businesses can ensure they are well-prepared for the challenges ahead.
Investing in robust cloud security practices, including strong identity and access management, compliance automation, and vendor risk management, is essential for protecting sensitive data. By adopting a comprehensive approach to cloud security, organizations can navigate the complexities of the digital landscape while safeguarding their assets and maintaining customer trust.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary cloud computing risks related to data breaches and leakage?
Cloud computing risks related to data breaches and leakage include unauthorized access to sensitive information due to weak authentication, misconfigured settings, and insecure APIs. Businesses must implement robust encryption methods and continuous monitoring to protect against these risks.
How can organizations mitigate insufficient identity and access management (IAM) risks in cloud computing?
To mitigate IAM risks, organizations should implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), regularly review user permissions, and adopt a zero trust architecture. This ensures that only authorized users have access to critical systems, reducing the risk of data leaks.
What precautions should be taken to address misconfiguration and insecure APIs in cloud environments?
Organizations should perform regular security scans to identify misconfigurations, utilize cloud-native security tools, enforce API security measures, and adhere to cloud configuration benchmarks to minimize risks associated with insecure APIs.
What are the compliance challenges organizations face in cloud computing?
Compliance challenges in cloud computing include adhering to regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Organizations must stay informed about regulatory changes, deploy compliance automation tools, and conduct regular audits to ensure they meet legal requirements.
How can businesses protect themselves from Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks in the cloud?
To protect against DDoS attacks, businesses should utilize DDoS mitigation tools provided by cloud vendors, install Web Application Firewalls (WAF), and develop incident response plans to quickly address any attack.
What risks do insecure third-party integrations pose in cloud computing?
Insecure third-party integrations can increase an organization’s attack surface. Regular assessments of third-party security controls and establishing robust vendor risk management frameworks are essential to mitigate these risks.
What strategies can help prevent data loss and recovery failures in the cloud?
To prevent data loss, organizations should implement version control, develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan, and ensure redundancy planning is in place to guarantee data availability even during outages.
What is cloud vendor lock-in and how can businesses avoid it?
Cloud vendor lock-in occurs when an organization becomes dependent on a single cloud provider, reducing flexibility. Businesses can avoid this by adopting a multi-cloud strategy and negotiating flexible contracts with their providers.
What emerging threats related to AI and automation should organizations be aware of in cloud computing?
Emerging threats include AI-driven cyberattacks that exploit automation vulnerabilities. Organizations should implement AI security frameworks and continuously monitor automated processes for unusual activities to mitigate these risks.
How important is cloud security for mitigating risks associated with cloud computing?
Cloud security is crucial for mitigating risks such as data breaches, compliance failures, and unauthorized access. Implementing proactive security measures helps protect sensitive data and maintain business integrity in the cloud.
| Risk Category | Description | Precautions and Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Data Breaches and Leakage | Sensitive data stored in the cloud is vulnerable to cybercriminals due to unauthorized access and weak authentication. | – Implement robust encryption for data at rest and in transit. – Disable access for users without multi-factor authentication. – Continuously monitor for unusual access patterns. |
| Insufficient Identity and Access Management (IAM) | Weak IAM policies can lead to unauthorized access and insider threats. | – Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). – Review user permissions regularly. – Implement zero trust architecture. |
| Misconfiguration and Insecure APIs | Misconfigurations create vulnerabilities for attackers. | – Conduct security scans for misconfigurations. – Use cloud-native security tools. – Enforce API security measures. |
| Compliance and Regulatory Challenges | Non-compliance with data protection regulations can lead to penalties. | – Stay informed on regulations. – Use compliance automation tools. – Conduct regular audits. |
| Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks | DDoS attacks can financially damage organizations and disrupt services. | – Utilize DDoS mitigation tools. – Install Web Application Firewalls (WAF). – Develop DDoS response plans. |
| Insecure Third-Party Integrations | Third-party applications increase the risk of cyberattacks. | – Assess third-party security controls. – Establish vendor risk management frameworks. – Deploy API gateways. |
| Data Loss and Recovery Failures | Data loss can occur from various issues, necessitating backup strategies. | – Implement version control for backups. – Develop disaster recovery plans. – Employ redundancy planning. |
| Cloud Vendor Lock-In | Relying on a single vendor reduces flexibility and increases risks. | – Adopt a multi-cloud strategy. – Negotiate flexible contracts. – Evaluate vendor performance regularly. |
| Emerging AI and Automation Threats | AI can create new vulnerabilities, leading to sophisticated attacks. | – Implement AI security frameworks. – Test AI models before deployment. – Monitor automated processes. |
Summary
Cloud computing risks are becoming increasingly significant as businesses transition to digital solutions. With the rise of cyber threats, organizations must prioritize robust security measures to combat potential vulnerabilities. By understanding the top cloud computing risks for 2025, such as data breaches, compliance challenges, and emerging AI threats, companies can implement proactive strategies to protect their data and maintain customer trust. Emphasizing security in cloud computing not only safeguards company assets but also ensures compliance with evolving regulations in an ever-changing digital landscape.