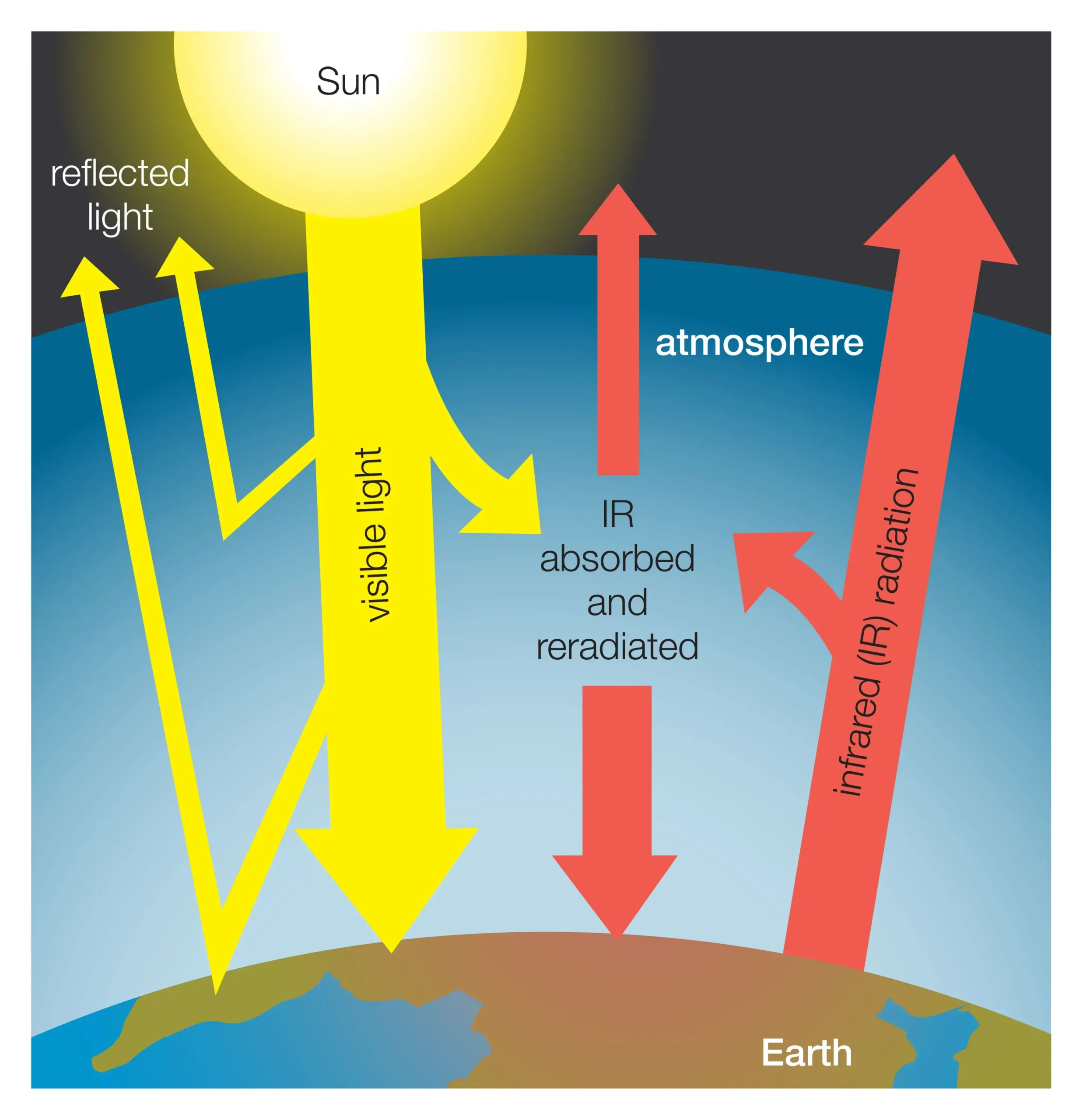
Global warming is an urgent and undeniable reality that threatens our planet’s delicate balance. As global temperatures continue to rise, we are witnessing the harrowing consequences of climate change, from devastating wildfires to unprecedented storms. Attribution science reveals how this increase in heat is not merely a statistic but a catalyst for extreme weather events that disrupt ecosystems and human communities alike. The climate crisis we face today is not just a future concern; it is a present-day emergency that demands immediate action. With each passing year, the evidence grows clearer that global warming is accelerating, and its adverse effects are becoming impossible to ignore.
The phenomenon of rising global temperatures is often referred to as climate change, a term that encapsulates the broader spectrum of environmental shifts impacting our planet. This escalating warmth is contributing to alarming trends in weather patterns, leading to increasingly severe and unpredictable atmospheric conditions. In scientific circles, the study of how human activities influence these changes is explored through attribution science, connecting the dots between our actions and their consequences on nature. The ongoing climate crisis underscores the urgency of addressing these issues as we confront more frequent and intense extreme weather events. Understanding this complex web of interactions is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate the impact of our warming world.
Understanding Global Warming: The Rising Temperature Crisis
Global warming is perhaps the most pressing environmental issue we face today. As Earth’s average temperature continues to rise at an unprecedented rate, the implications of this phenomenon are becoming increasingly evident. The past few decades have shown a clear trend of global temperature rise, driven largely by human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. These actions have resulted in an increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which trap heat and exacerbate climate change, leading to severe consequences for ecosystems and human societies alike.
Attribution science plays a crucial role in understanding the impacts of global warming, particularly in analyzing extreme weather events. By linking specific weather events to the broader context of climate change, scientists can illustrate how rising temperatures contribute to more intense storms, droughts, and wildfires. For instance, the recent surge in catastrophic hurricanes and wildfires can be attributed to the warmer, more volatile climate created by global warming. This connection between temperature rise and extreme weather events underscores the urgent need to address the climate crisis before it spirals further out of control.
The Role of Attribution Science in Climate Change
Attribution science is an innovative field that seeks to quantify the influence of climate change on specific weather events. By utilizing sophisticated models and historical data, scientists can determine the likelihood that a particular event, such as a heatwave or heavy rainfall, was exacerbated by human-induced climate change. This scientific approach not only enhances our understanding of climate impacts but also helps policymakers and the public grasp the urgency of addressing global warming.
For instance, the wildfires that ravaged California in recent years were not just a result of natural weather patterns but were significantly worsened by climate change. Increased temperatures led to prolonged dry spells and more intense Santa Ana winds, creating the perfect conditions for devastating fires. Attribution science allows researchers to communicate these complex relationships effectively, highlighting how global warming directly contributes to the frequency and severity of extreme weather events. This knowledge is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate climate change impacts.
Extreme Weather Events: The Consequences of Rising Temperatures
As global temperatures continue to rise, the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events are also increasing. This troubling trend has been observed across the globe, from hurricanes and typhoons to droughts and floods. Warmer air holds more moisture, which can lead to heavier rainfall and increased flooding, while higher ocean temperatures fuel more powerful storms. These changes have devastating effects on communities, economies, and ecosystems, making it imperative that we take action to combat climate change.
The aftermath of such extreme weather events can be catastrophic, resulting in loss of life, displacement of populations, and significant economic damages. For example, Hurricane Ida caused widespread destruction in the United States, while Typhoon Gaemi wreaked havoc in the Philippines. These disasters serve as stark reminders of the urgent need to address the climate crisis. As we continue to experience the fallout from global warming, it is clear that immediate and sustained action is necessary to mitigate these impacts and protect future generations.
The Climate Crisis: Urgency for Action
The term ‘climate crisis’ has become increasingly prominent in discussions about global warming and its effects. This phrase captures the reality that the consequences of climate change are not just looming threats for the future; they are present challenges that we must confront now. Rising sea levels, melting glaciers, and extreme weather events are just a few examples of the urgent issues we face as a result of our warming planet. The climate crisis demands immediate attention and action from governments, businesses, and individuals worldwide.
Addressing the climate crisis requires a multifaceted approach that includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and implementing sustainable practices across all sectors. Public awareness and education are essential in driving change, as individuals can contribute to solutions through lifestyle choices and advocacy. The longer we wait to address global warming, the more severe the impacts will be, making it essential that we act decisively to mitigate the climate crisis.
Data Analysis: Visualizing Global Warming Trends
Data analysis plays a critical role in understanding the trends and implications of global warming. By examining vast amounts of temperature data collected over time, scientists can visualize the alarming rate at which our planet is heating. The use of graphs and charts can transform complex datasets into accessible information that illustrates how the Earth’s temperature has changed since reliable measurements began in the late 19th century. Such visualizations serve not only as a means of communication but also as a call to action.
For instance, a chart depicting monthly global temperatures since 1880 can reveal a clear upward trend, emphasizing the necessity for immediate climate action. These visual tools highlight the stark reality of global warming and can foster a greater sense of urgency among policymakers and the public. By providing an undeniable representation of temperature rise, data analysis supports the argument that we cannot afford to ignore the consequences of our actions on the environment.
The Importance of Reliable Climate Data
Reliable climate data is foundational to understanding global warming and its impacts. Organizations like NASA and NOAA have dedicated resources to collecting and analyzing climate data, providing a comprehensive picture of the changing climate. This data, collected from a variety of sources including land-based monitoring stations and ocean buoys, allows scientists to track temperature changes accurately and identify trends over time. The reliability of this data is crucial for informing climate policy and public awareness.
Moreover, the use of standardized baselines in climate data analysis helps provide context for understanding temperature anomalies. For example, comparing current temperatures to historical averages from specific periods can indicate how much the climate has shifted. Understanding these shifts is essential for addressing the ongoing challenges of global warming and developing strategies to mitigate its effects. Accurate climate data not only informs scientific research but also empowers communities to make informed decisions regarding climate adaptation and resilience.
Global Warming: A Call for Sustainable Solutions
The alarming reality of global warming necessitates a collective response toward sustainable solutions. As we witness the detrimental effects of climate change, it becomes increasingly clear that transforming our energy systems, transportation methods, and agricultural practices is crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Innovations in renewable energy, such as solar and wind power, present viable alternatives to fossil fuels, which are major contributors to global warming. By investing in these sustainable options, we can significantly lessen our environmental impact.
Moreover, adopting sustainable practices in daily life can empower individuals to contribute to the fight against global warming. Simple actions like reducing waste, conserving energy, and supporting eco-friendly products can make a substantial difference when embraced on a larger scale. As awareness grows regarding the climate crisis, it is imperative that everyone plays a role in promoting sustainability, ensuring that future generations inherit a healthier planet.
The Global Response to Climate Change
The global response to climate change has evolved significantly over the past few decades, with international agreements such as the Paris Agreement aiming to unite nations in the fight against global warming. This landmark accord sets ambitious targets for limiting global temperature rise and encourages countries to develop their strategies for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The collaborative nature of these efforts highlights the understanding that climate change is a global challenge that requires collective action.
However, progress has been uneven, and many countries are still struggling to meet their commitments. The urgency of the situation calls for increased accountability and innovative policies that drive meaningful change. By leveraging technology, investing in green infrastructure, and promoting sustainable practices, nations can work together to combat global warming effectively. The global response to climate change is not just a moral imperative; it is essential for the survival and prosperity of future generations.
The Future of Our Planet: Navigating the Climate Crisis
As we look toward the future, the trajectory of our planet hinges on our ability to navigate the climate crisis effectively. The impacts of global warming are projected to intensify if current trends continue, leading to more frequent and severe weather events, loss of biodiversity, and significant socio-economic challenges. It is crucial that we not only acknowledge these consequences but also take proactive measures to avert the worst outcomes of climate change.
This requires a shift in mindset from viewing climate change as a distant threat to recognizing it as an immediate challenge that demands urgent action. By fostering a culture of sustainability and resilience, we can work towards a future where communities are better equipped to adapt to changing conditions. It is imperative that we harness innovation, collaborate on solutions, and commit to a sustainable path forward for the health of our planet and future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is global warming and how does it relate to climate change?
Global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases. It is a significant aspect of climate change, which encompasses broader shifts in weather patterns, including increased frequency of extreme weather events.
How does global warming contribute to extreme weather events?
Global warming intensifies extreme weather events by altering atmospheric conditions. Warmer air holds more moisture, leading to heavier rainfall and increased flooding, while warmer ocean temperatures provide more energy for storms, resulting in more powerful hurricanes and typhoons.
What role does attribution science play in understanding global warming?
Attribution science helps determine the extent to which human-induced global warming influences specific weather events. It analyzes how climate change impacts natural weather patterns, providing evidence that supports the connection between rising global temperatures and increased intensity of events like wildfires and hurricanes.
What are the potential impacts of global warming on future weather patterns?
Global warming is expected to lead to more frequent and severe extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, heavy precipitation, and droughts. These changes can disrupt ecosystems, agriculture, and human settlements, exacerbating existing climate crises.
How fast is global warming happening, and what data supports this?
Global warming is occurring at an unprecedented rate, with the Earth experiencing significant temperature rises since the mid-20th century. Data from NASA and NOAA shows that average global temperatures have increased markedly since 1880, with accelerating rates observed since 1970.
What measures can be taken to mitigate the effects of global warming?
Mitigating global warming involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy sources, increasing energy efficiency, and implementing carbon capture technologies. Additionally, protecting and restoring natural ecosystems can help absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Why is the 1.5°C threshold significant in discussions about global warming?
The 1.5°C threshold, outlined in the Paris Agreement, is critical because exceeding this limit significantly increases the risks of severe climate impacts. Keeping global temperature rise below this threshold is essential to avoid catastrophic effects on ecosystems and human societies.
What is the climate crisis and how does it relate to global warming?
The climate crisis refers to the urgent and escalating impacts of climate change caused largely by global warming. It highlights the immediate need for action to address the adverse effects of rising temperatures, such as extreme weather, rising sea levels, and biodiversity loss.
How does global warming affect sea levels?
Global warming leads to rising sea levels through thermal expansion of seawater and melting of ice sheets and glaciers. As global temperatures rise, polar ice caps melt, contributing to higher ocean levels that threaten coastal communities and ecosystems.
What can individuals do to combat global warming?
Individuals can combat global warming by reducing energy consumption, using public transportation, supporting renewable energy initiatives, minimizing waste, and advocating for policies that address climate change. Every small action contributes to a larger global effort.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Earth’s Temperature Rise | Global temperatures are rising at an unprecedented rate, with recent years being the warmest since reliable record-keeping began. |
| Attribution Science | This field studies how climate change affects natural weather cycles, leading to extreme weather events like wildfires and hurricanes. |
| Impact of Global Warming | Rising temperatures contribute to more intense storms and extreme weather, resulting in significant damage and loss of life. |
| Data Analysis | Visualizations illustrate the rapid temperature increases over time, highlighting the acceleration of global warming. |
| Global Warming Crisis | The effects of climate change are immediate and severe, marking the current era as a climate crisis that demands urgent action. |
Summary
Global warming is an urgent issue that affects our planet today more than ever. The alarming rise in Earth’s temperatures is a clear indicator of the climate crisis we face. With extreme weather events becoming more frequent and intense, it is crucial to understand the underlying factors of global warming and take proactive measures to mitigate its impacts.