RAN virtualization is revolutionizing the landscape of mobile communications, particularly with the advent of 5G networks and beyond. By optimizing resource management and addressing energy costs, RAN virtualization, including concepts like Virtual RAN (V-RAN) and Cloud RAN (C-RAN), enhances the efficiency of radio access networks. Despite promising trials globally, the full potential of V-RAN remains largely untapped due to various limitations within current platforms. The ongoing pursuit of Open RAN solutions is paving the way for greater flexibility and scalability in Base Band Unit (BBU) deployment, which is critical for future innovations in network virtualization. This article delves into the latest advancements in RAN virtualization and the challenges that still need to be overcome to realize its full capabilities.
In the realm of telecommunications, the virtualization of radio access networks (RAN) is a pivotal development that supports the transition towards more dynamic and efficient network architectures. Often referred to as Virtual RAN (V-RAN), and encompassing frameworks like Cloud RAN (C-RAN) and Open RAN, this innovation allows for streamlined operations and improved resource allocation. The evolution of these technologies is essential for addressing the complexities of network management and optimizing energy consumption. As we explore the intricacies of this transformation, it becomes evident that the scalability of Base Band Units (BBUs) and the implementation of network virtualization strategies will play a crucial role in shaping the future of mobile connectivity. This discussion aims to provide insights into the current state and future prospects of RAN virtualization.
Understanding RAN Virtualization in 5G Networks
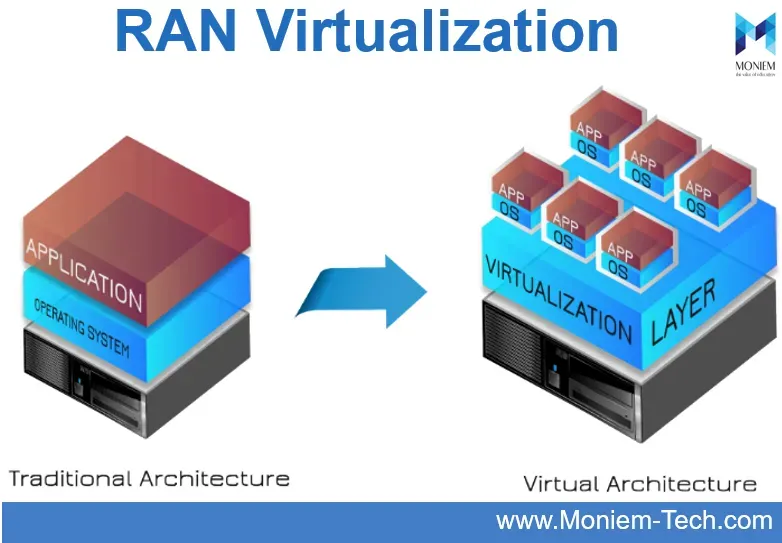
RAN virtualization is a transformative approach in the realm of 5G networks, facilitating the optimization of resource management and addressing the escalating energy costs associated with mobile communications. By separating hardware from software, RAN virtualization enables the creation of flexible, scalable, and efficient network architectures. This decoupling allows operators to dynamically allocate resources based on demand, leading to improved performance and lower operational costs. As the telecommunications industry evolves, understanding the fundamentals of RAN virtualization becomes essential for stakeholders aiming to leverage the full potential of next-generation networks.
Furthermore, the shift towards RAN virtualization aligns with the industry’s broader move towards cloud-based solutions and greater network flexibility. Concepts such as Cloud RAN (C-RAN) and Open RAN are integral to this transition, providing the necessary frameworks for deploying virtualized RAN architectures. By employing these technologies, operators can enhance their network’s agility, allowing them to respond swiftly to changing market conditions and consumer demands. This adaptability is vital in an era where the demands on wireless networks are increasing exponentially.
Exploring the Variants of RAN Virtualization
RAN virtualization encompasses various models, each offering distinct advantages and operational efficiencies. Full virtualization, for instance, supports diverse operating systems on a single hardware platform, ensuring high levels of resource utilization and user isolation. This model, however, can lead to performance bottlenecks due to the overhead associated with managing multiple virtual machines. On the other hand, para-virtualization allows guest systems direct access to hardware, which can significantly enhance performance, making it particularly suitable for high-demand applications.
Application virtualization and OS virtualization represent additional paradigms within the RAN virtualization landscape, each aiming to optimize network operations. Application virtualization facilitates centralized management of applications while enhancing remote access capabilities. OS virtualization, through its use of containers, allows for improved system performance and resource allocation efficiency. Network virtualization, in particular, abstracts physical network resources, enabling the creation of multiple independent virtual networks, thus fostering innovation and service differentiation.
The Evolution of V-RAN and Its Impact on Network Services
The evolution of Virtual RAN (V-RAN) marks a significant advancement in the architecture of radio access networks, transitioning from traditional centralized RAN (C-RAN) models to more flexible and efficient structures. V-RAN aims to optimize the allocation of resources, enabling operators to enhance throughput and energy efficiency while simultaneously reducing operational costs. This shift is crucial as mobile data consumption continues to surge, necessitating more adaptive and resilient network solutions.
Architectural proposals for V-RAN emphasize the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, which can further enhance resource management and operational efficiency. By employing these technologies, V-RAN can support intelligent decision-making processes that optimize network performance in real-time. This not only improves user experience but also paves the way for innovative services and applications that leverage the enhanced capabilities of virtualized networks.
Challenges in Implementing V-RAN Solutions
Despite the promising advancements in V-RAN, several challenges hinder its full implementation across networks. One major issue is the lack of flexibility in current network functions, which limits the modularity and orchestration required among virtual Base Band Units (BBUs). These limitations can lead to inefficiencies and complexity in managing network resources, ultimately impacting service quality and operational performance.
Moreover, scalability issues concerning BBUs pose significant hurdles for operators. As networks expand and the demand for bandwidth increases, ensuring that BBUs can support additional loads without compromising performance becomes critical. Addressing these scalability concerns is essential for the successful deployment of V-RAN, as it directly impacts the ability to deliver seamless and high-quality services to consumers.
The Role of Open RAN in Network Virtualization
Open RAN plays a pivotal role in the broader context of network virtualization, promoting interoperability and innovation within the telecommunications ecosystem. By adopting open standards and interfaces, Open RAN facilitates the integration of diverse vendor solutions, allowing operators to tailor their networks according to specific operational needs. This flexibility is crucial in enabling the deployment of virtualized RAN solutions that can adapt to evolving market demands.
The collaboration fostered by Open RAN initiatives also encourages competition among vendors, driving down costs and accelerating the pace of technological advancements. As operators increasingly seek to implement RAN virtualization, the principles of Open RAN will be instrumental in ensuring that these deployments are efficient, scalable, and future-proof. Ultimately, embracing Open RAN will enhance the overall performance of virtualized networks, contributing to the successful realization of 5G and beyond.
Future Directions in RAN Virtualization
Looking ahead, the future of RAN virtualization is poised for remarkable growth as technology continues to evolve. Innovations in cloud computing and edge computing will further enhance the capabilities of virtualized networks, enabling operators to deliver high-performance services with minimal latency. As the demand for faster and more reliable connections increases, the implementation of advanced virtualization techniques will become essential for maintaining competitive advantages in the telecommunications sector.
Additionally, ongoing research and development efforts will focus on overcoming existing challenges associated with V-RAN and network virtualization. This includes addressing issues related to BBU scalability, orchestration, and resource management, which have hindered full implementations thus far. By investing in these areas, the telecommunications industry can unlock the full potential of RAN virtualization, leading to transformative changes in how networks are designed, operated, and maintained.
Impact of RAN Virtualization on Cost Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of RAN virtualization is its ability to enhance cost efficiency for operators. By transitioning from traditional hardware-based systems to virtualized models, telecom companies can significantly reduce capital expenditures and operational costs. Virtualized systems allow for better resource allocation, minimizing the need for extensive physical infrastructure while maximizing the utilization of existing assets.
Moreover, the scalability offered by virtualized RAN infrastructures means that operators can more easily adjust their resources based on fluctuating demand. This adaptability not only leads to cost savings but also enhances the overall resilience of the network. As operators face the pressures of increasing data consumption and evolving customer expectations, the financial benefits of RAN virtualization will become increasingly crucial in maintaining profitability.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency through RAN Virtualization
In an era where energy costs are rising and environmental sustainability is becoming a priority, RAN virtualization offers a pathway to enhanced energy efficiency. By optimizing the allocation of resources and enabling dynamic scaling of network components, virtualized RAN systems can significantly reduce energy consumption. This is particularly important as networks expand to accommodate the growing demand for mobile data.
Furthermore, the centralized management capabilities of virtualized networks allow operators to implement energy-saving strategies more effectively. For instance, resources can be shifted to consolidate traffic during off-peak hours, minimizing energy usage without sacrificing performance. As the telecommunications industry continues to prioritize sustainability, RAN virtualization will play a crucial role in achieving these energy efficiency goals.
Implementing V-RAN: A Guide for Operators
For operators looking to implement Virtual RAN (V-RAN), it is essential to adopt a structured approach that considers the unique requirements of their network environments. A comprehensive assessment of existing infrastructure and an understanding of the specific benefits of V-RAN are critical first steps. Operators must evaluate their current capabilities in terms of hardware, software, and operational processes to identify areas that can be optimized through virtualization.
Additionally, collaboration with technology vendors and participation in industry initiatives can provide valuable insights and resources for successful V-RAN implementation. Engaging with open-source communities and adopting Open RAN principles can further enhance the flexibility and scalability of the deployed solutions. By taking these steps, operators can ensure a smooth transition towards V-RAN, positioning themselves to capitalize on the numerous advantages it offers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RAN virtualization and its significance in modern networks?
RAN virtualization refers to the process of decoupling hardware and software components in the Radio Access Network (RAN), allowing for more flexible and efficient management of network resources. Its significance lies in optimizing resource allocation and reducing operational costs, especially in the context of 5G and beyond.
How does Virtual RAN (V-RAN) differ from Cloud RAN (C-RAN)?
Virtual RAN (V-RAN) operates by virtualizing baseband processing functions, enhancing flexibility and scalability, whereas Cloud RAN (C-RAN) centralizes processing in a cloud infrastructure. Both aim to improve network efficiency but differ in their deployment architectures and resource management approaches.
What are the benefits of implementing Open RAN in RAN virtualization?
Open RAN promotes interoperability among different vendors’ equipment, fostering innovation and reducing vendor lock-in. By implementing Open RAN within RAN virtualization, operators can achieve increased flexibility, lower costs, and enhanced network performance.
What challenges does V-RAN face in terms of Base Band Unit (BBU) scalability?
V-RAN faces challenges regarding BBU scalability, as current platforms often lack the flexibility for modular growth. This restricts the ability to efficiently scale network capacity in response to demand changes, limiting the effectiveness of virtualized network solutions.
Can RAN virtualization help in managing energy costs for telecom operators?
Yes, RAN virtualization can significantly help manage energy costs by optimizing resource management and enabling dynamic scaling of network resources. This leads to reduced energy consumption, which is crucial as operators seek to lower operational expenses and improve sustainability.
What role does network virtualization play in the evolution of V-RAN?
Network virtualization is a foundational component of V-RAN, allowing for the abstraction of network resources from the physical hardware. This enables the deployment of multiple virtual networks on a single infrastructure, enhancing flexibility and resource utilization in V-RAN implementations.
How do current vendor platforms limit the implementation of V-RAN?
Current vendor platforms often limit V-RAN implementations by lacking modularity and flexibility in network functions. Additionally, orchestration among different virtual Base Band Units (BBUs) can be inadequate, impacting the overall efficiency and performance of the virtualized network.
What is the future outlook for RAN virtualization technologies?
The future outlook for RAN virtualization technologies is promising, with ongoing research aimed at overcoming existing challenges. As the industry continues to innovate, we can expect advancements in interoperability, scalability, and energy efficiency, facilitating broader adoption of V-RAN and related technologies.
| Key Points | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| RAN Virtualization | A key concept in 5G networks, optimizing resource management and addressing energy costs. | |
| Virtual RAN (V-RAN) | An evolution of C-RAN aiming for flexible resource allocation and efficiency. | |
| Implementation Challenges | Current platforms face limitations in modularity, scalability, and orchestration of virtual Base Band Units (BBUs). | |
| Types of Virtualization | Includes Full Virtualization, Para-Virtualization, Application Virtualization, OS Virtualization, and Network Virtualization. | |
| Financial Benefits | Reduces acquisition and maintenance costs, enhancing overall hardware utilization. | |
Summary
RAN virtualization is a transformative approach in modern telecommunications, particularly within the 5G framework. By embracing virtualization technologies, network operators can optimize resource management while addressing crucial challenges such as energy costs and operational efficiency. Although significant advancements have been made, the successful implementation of Virtual RAN (V-RAN) hinges on overcoming existing limitations and enhancing flexibility within network architectures. The focus on V-RAN will be pivotal for the future of mobile networks, ensuring that they meet the demands of a rapidly evolving digital landscape.