Windows 11 adoption issues have become a prominent topic in the tech community, sparking discussions about why users remain hesitant to make the switch from Windows 10. Despite a slight increase in Windows 11’s market share recently, many users still find themselves clinging to the familiarity and reliability of Windows 10. The stringent Windows 11 hardware requirements, including the need for a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) and compatible CPUs, have posed significant upgrade challenges for countless users, resulting in a divided user base. Furthermore, a lack of compelling features in Windows 11 compared to Windows 10 has left many users questioning whether the upgrade is truly worth it. As the deadline for Windows 10 support approaches, the question remains: will these adoption issues resolve, or will users continue to resist the change?
The challenges surrounding the transition to Microsoft’s latest operating system, often referred to as Windows 11 upgrade challenges, reflect a broader struggle for users weighing the pros and cons of upgrading. Many individuals are caught in the Windows 10 vs Windows 11 debate, unsure if the new features justify the migration. The stringent hardware requirements set by Microsoft have left many existing systems incompatible, thus stalling the adoption rate and impacting Windows 11 market share growth. Additionally, the comparison of Windows 11 features against those available in Windows 10 highlights a lack of standout innovations that would entice users to upgrade. As businesses and individuals consider their options, the ongoing discussion about Windows 11 adoption issues continues to evolve.
Understanding Windows 11 Adoption Issues
The adoption of Windows 11 has been a contentious topic since its launch in 2021. Despite slight increases in market share, many users remain hesitant to transition from Windows 10. One of the primary reasons for this reluctance is the stringent hardware requirements that Microsoft has imposed. With the need for a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 and a compatible CPU, a significant portion of existing hardware was rendered obsolete, leading to frustration among users who felt compelled to upgrade their machines to meet the new standards.
Another contributing factor to the adoption issues is the lack of compelling features that differentiate Windows 11 from its predecessor. Many users realize that the enhancements introduced in Windows 11, such as improved security and specific user interface changes, are not drastically different from what they can achieve in Windows 10. For organizations that have effectively managed their Windows 10 environments, the perceived risks associated with upgrading to Windows 11 make sticking with the older OS a more attractive option.
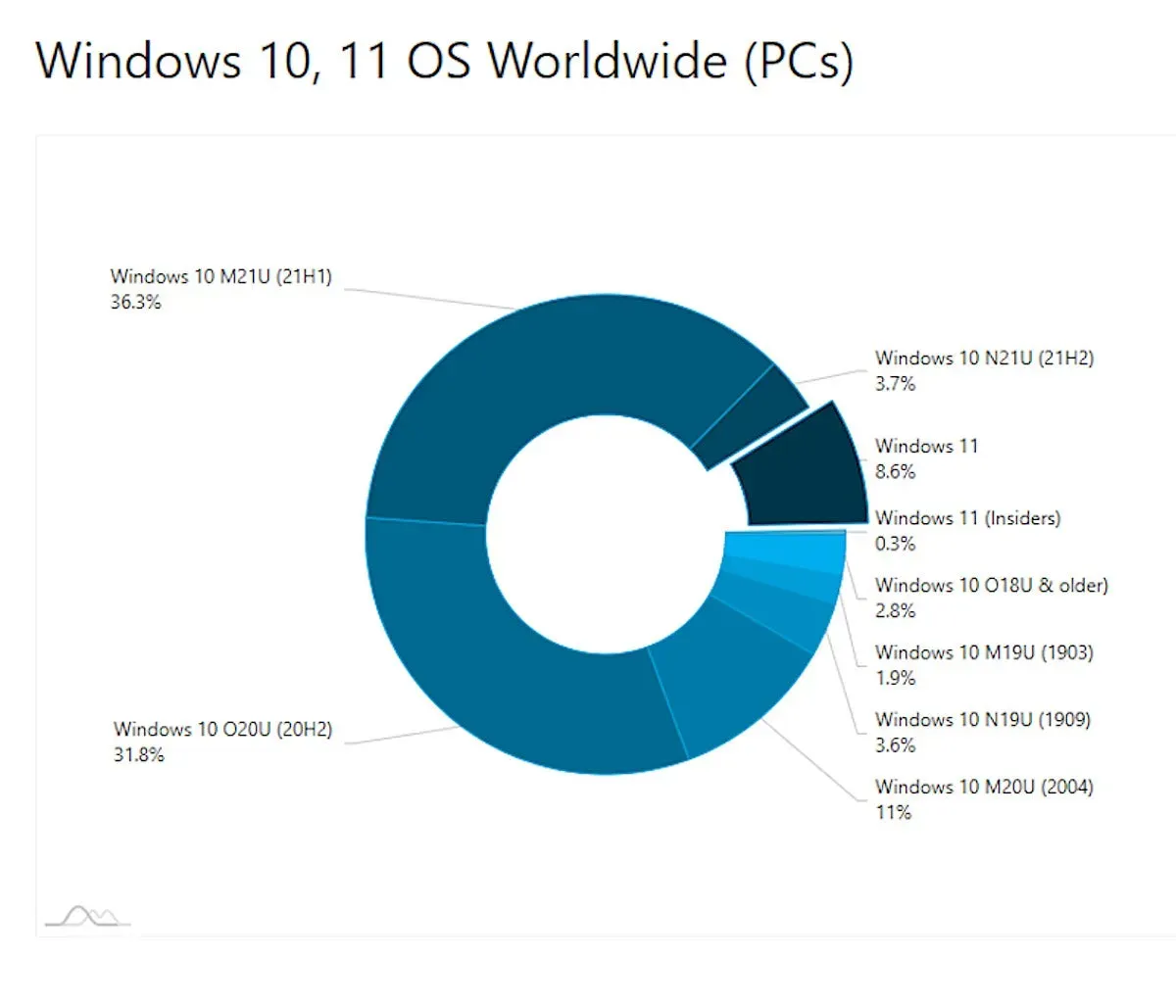
Windows 10 vs Windows 11: Market Share Dynamics
As of now, Windows 10 continues to dominate the market share despite the release of Windows 11. This trend can be attributed to several factors, including the established familiarity users have with Windows 10 and the perception that it meets their needs without the complications associated with the new OS. The comparative analysis between Windows 10 and Windows 11 shows that while the latter introduces some new features, it does not offer enough of a leap in functionality to justify the transition for many users.
Additionally, the ongoing support for Windows 10 until October 14, 2025, allows users to feel secure in their decision to remain with the current operating system. This timeline creates a cushion for businesses to consider their options without the pressure of immediate upgrades. Microsoft’s emphasis on maintaining security and functionality in Windows 10 has established a loyal user base that is less inclined to migrate to Windows 11 until a significant incentive is presented.
Windows 11 Hardware Requirements: A Barrier to Adoption
The hardware requirements for Windows 11 have been a significant barrier for many users. Microsoft’s decision to enforce these requirements means that a considerable number of existing PCs are incompatible with the new OS. Users are often frustrated by the realization that their devices, which were perfectly functional under Windows 10, are suddenly deemed obsolete due to the new TPM and CPU specifications. This situation has led to reluctance among consumers to invest in new hardware solely for the purpose of upgrading to Windows 11.
Moreover, the hardware landscape is gradually changing. As time passes, more users are encountering situations where purchasing a new PC inevitably leads to Windows 11 compatibility. However, given the historical context of upgrades, many are still hesitant to make the leap until they feel confident that the benefits of Windows 11 will outweigh the investment in new hardware. The combination of financial considerations and the perceived value of the upgrade continues to keep many users firmly entrenched in the Windows 10 ecosystem.
Windows 11 Upgrade Challenges: User Experiences
Many users have reported various challenges when attempting to upgrade to Windows 11. Issues such as missing user interface elements and connectivity problems have plagued the upgrade experience, leading some to revert back to Windows 10. For example, the frustrations surrounding taskbar positioning and Wi-Fi connectivity have prompted users to question whether the upgrade was worth the hassle. This negative feedback has contributed to a broader narrative that reinforces the reluctance to adopt Windows 11.
Additionally, the challenges encountered during the upgrade process highlight a crucial aspect of user experience: the expectation for a seamless transition. Users who have invested time and resources into their current operating systems expect that any upgrade will bring about tangible improvements without disrupting their workflow. Unfortunately, for many, Windows 11 has not delivered on this expectation, resulting in a cautious approach towards the new operating system.
Windows 11 Features Comparison: What’s New?
When comparing the features of Windows 10 and Windows 11, it becomes apparent that many of the enhancements introduced in the new OS can be replicated in Windows 10 with the right configurations. For instance, while Windows 11 comes with BitLocker enabled by default, savvy users can achieve similar security measures on Windows 10 without needing to transition to the new system. This overlap in functionality diminishes the urgency to upgrade for many users, particularly those who prioritize stability over novelty.
Furthermore, the user interface changes in Windows 11, while aesthetically pleasing, do not necessarily translate into improved productivity or usability for every user. Many individuals have grown accustomed to the Windows 10 interface and prefer not to adapt to the new layouts and features without a clear benefit. As a result, the lack of a standout feature that compels users to migrate continues to hinder Windows 11’s adoption in a market that remains heavily influenced by user experience and familiarity.
The Future of Windows: Transition Timeline
Microsoft has set a clear timeline for the eventual transition from Windows 10 to Windows 11, with the end of support date for Windows 10 looming in 2025. This deadline creates a sense of urgency for businesses and individuals to consider upgrading to ensure compliance and continued support. However, the effectiveness of this strategy remains to be seen, as many users are still skeptical about the advantages of making the switch.
The anticipation of a wave of upgrades driven by the end-of-support date could be overshadowed by the ongoing concerns regarding the user experience and hardware compatibility. As Microsoft pushes for wider adoption of Windows 11, it will need to provide substantial incentives that demonstrate the value of the upgrade beyond mere compliance. The future of Windows hinges on addressing these user concerns while showcasing the long-term benefits of embracing the new operating system.
Marketing Windows 11: The Role of AI
In light of the challenges surrounding Windows 11 adoption, Microsoft’s marketing teams are shifting their focus toward the emerging trend of AI PCs. This pivot reflects an industry-wide recognition that the allure of artificial intelligence could serve as a catalyst for renewed interest in Windows 11. However, similar to Windows 11, the lack of a compelling ‘killer app’ that drives users to local AI solutions presents a significant challenge.
The focus on AI also raises questions about pricing and accessibility. As manufacturers explore ways to integrate AI capabilities into their devices, users are left wondering what the added value will be and how it will impact their overall computing experience. Without clear advantages that resonate with consumers, the push towards AI PCs may face similar resistance as the transition to Windows 11, underscoring the importance of aligning product offerings with user needs and expectations.
The Importance of User Feedback in Upgrades
User feedback has emerged as a critical component in the dialogue surrounding Windows 11’s adoption. As many users have voiced concerns about their upgrade experiences, it’s essential for Microsoft to listen and respond to these critiques in order to build trust and improve the overall user experience. Addressing common pain points, such as user interface frustrations and hardware compatibility, could significantly impact the perception and adoption rates of Windows 11.
Moreover, engaging with users through surveys and feedback channels can provide valuable insights into what features or changes might motivate individuals to upgrade. By prioritizing user feedback, Microsoft can make informed decisions that align with consumer expectations and drive a more favorable response to Windows 11. Ultimately, fostering a collaborative relationship with users could pave the way for a smoother transition to the new operating system.
Navigating the Transition: Strategies for IT Departments
For many organizations, the transition to Windows 11 is not merely a choice but a necessity due to the impending end of support for Windows 10. IT departments must navigate this transition strategically to minimize disruptions and ensure compliance. This includes assessing the current hardware inventory and evaluating which devices can be upgraded without incurring significant costs. By developing a phased approach to upgrades, IT teams can prioritize devices that are most critical to business operations.
Additionally, providing training and resources for end-users can help alleviate concerns associated with the transition. By preparing employees for the changes they will encounter in Windows 11, organizations can foster a more positive reception to the upgrade process. Clear communication regarding the benefits of the new operating system and the support available during the transition can help ease the apprehensions that many users may have about moving away from a familiar environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main Windows 11 adoption issues users are facing?
Many users are experiencing adoption issues with Windows 11 primarily due to its stringent hardware requirements and the lack of compelling features that differentiate it from Windows 10. The necessity for a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 and a compatible CPU has excluded many existing machines, leading to frustrations and reluctance to upgrade.
How does Windows 10 compare to Windows 11 in terms of market share?
Despite a slight increase in Windows 11’s market share, Windows 10 maintains a significant lead. Many users find that Windows 10 meets their needs effectively, with most features available by simply enabling them, making the transition to Windows 11 less appealing.
What hardware requirements are necessary for Windows 11 adoption?
Windows 11 requires specific hardware, including a TPM 2.0 chip and a compatible CPU. This has been a barrier to adoption, as many older PCs do not meet these requirements, limiting the upgrade potential for a large segment of users.
What challenges do users face when upgrading to Windows 11?
Users often encounter upgrade challenges such as missing user interface elements, connectivity issues, and overall dissatisfaction with the new system. These problems have led some users to revert back to Windows 10 after experiencing difficulties.
Are there any compelling features in Windows 11 that encourage users to adopt it?
Currently, there are no standout features in Windows 11 that strongly motivate users to upgrade from Windows 10. Many functionalities available in Windows 11 can also be found in Windows 10, leading to a lack of urgency for users to make the switch.
What is Microsoft’s stance on Windows 11’s hardware requirements?
Microsoft has been firm in maintaining the hardware requirements for Windows 11, despite criticism. The company believes these requirements enhance security, but this has contributed to slow adoption rates as many users are hesitant to upgrade their hardware.
What is the predicted future for Windows 11 adoption?
While Microsoft aims to increase Windows 11 adoption, many users are resistant due to the lack of compelling reasons to upgrade and the challenges they face with existing hardware. The upcoming end of support for Windows 10 may eventually push more users to upgrade, but the transition seems gradual.
How will the end of support for Windows 10 affect Windows 11 adoption?
With Windows 10 support ending on October 14, 2025, many organizations may feel pressured to upgrade to Windows 11 to avoid compliance issues. However, unless Microsoft offers more compelling features or incentives, the adoption rate may still be slow.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| User Resistance | Users are hesitant to adopt Windows 11, comparing its marketing to selling ‘sand at a beach’. |
| Hardware Compatibility Issues | Windows 11 has strict hardware requirements, including TPM 2.0 and recent CPUs, limiting its adoption. |
| Market Share Comparison | Windows 10 retains a significant market share over Windows 11, despite some increases for the latter. |
| Lack of Compelling Features | Many features in Windows 11 are already present in Windows 10, reducing the incentive to upgrade. |
| User Experience Issues | Users have reported missing interface features and bugs, leading some to downgrade back to Windows 10. |
| Microsoft’s Stance | Microsoft maintains its hardware requirements and plans to push Windows 11 on users despite resistance. |
| Future Outlook | The end of support for Windows 10 in 2025 may compel upgrades, but clear benefits for users are still needed. |
Summary
Windows 11 adoption issues highlight a significant struggle for Microsoft in persuading users to transition from Windows 10. Despite some market share increases, many users remain resistant due to strict hardware requirements, lack of compelling features, and frustrating user experiences. As Windows 10 approaches its end of support, Microsoft faces the challenge of demonstrating the value of Windows 11 beyond mere compliance, necessitating a more effective strategy to encourage upgrades in the future.